概念 #
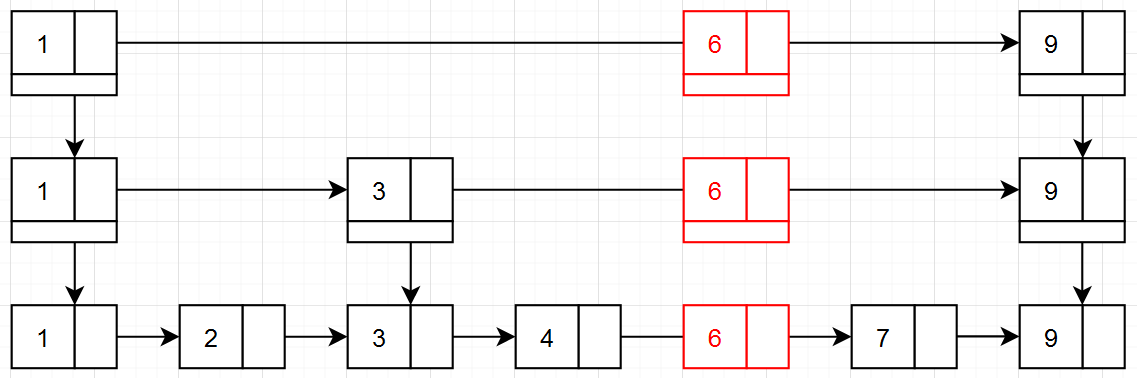
跳表是一种基于链表的动态数据结构,它允许快速地进行查找、插入和删除操作,且实现相对简单。跳表通过在链表的不同层级上建立索引,从而提高了查找效率。跳表的基本思想是在原始链表的基础上建立多层索引,每一层索引都是原始链表的子集,且越高层的索引节点越稀疏。
跳表的节点结构如下面代码中所示,每个节点包含一个键值对以及指向下一层的指针数组,其中 forward[ i ] 表示这个 node 指向跳表第 i 层的下一个节点,也就说说普通的链表 node 都是只有一个 next 节点,而跳表的 node 每一层都有一个 next 节点。跳表的层级是动态的,随着插入操作的进行而逐渐增加。在跳表中,每个节点都包含一个层级属性,表示它在跳表中所处的层数。
#define MAX_LEVEL 6
typedef struct SkipListNode {
int key;
int value;
struct SkipListNode *forward[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
} SkipListNode;
typedef struct SkipList {
int level;
SkipListNode *header;
} SkipList;
SkipListNode *createNode(int key, int value, int level) {
SkipListNode *newNode = (SkipListNode *)malloc(sizeof(SkipListNode));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
for (int i = 0; i <= level; i++) {
newNode->forward[i] = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
SkipList *createSkipList() {
SkipList *skipList = (SkipList *)malloc(sizeof(SkipList));
skipList->level = 0;
skipList->header = createNode(-1, -1, MAX_LEVEL);
return skipList;
}
跳表的插入操作通过随机生成一个层数,并将新节点插入到对应的层级链表中。
int randomLevel() {
int level = 0;
while (rand() < RAND_MAX / 2 && level < MAX_LEVEL) {
level++;
}
return level;
}
下面的代码中 insert 函数首先从最高层开始往下查找,对于第 i 层来说,如果当前节点的 key 小于要插入节点的 key,就在这一层往下查找。这一层最后遍历到的节点的值要么是 NULL, 要么 key 的值是第一个大于要插入的 key 的值,同时把这个 key 对应的 node 更新到 update 数组中。
然后调用 randomLevel() 函数得到了新的层数去插入,完整的函数如下:
void insert(SkipList *skipList, int key, int value) {
SkipListNode *update[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
SkipListNode *current = skipList->header;
for (int i = skipList->level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] != NULL && current->forward[i]->key < key) {
current = current->forward[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
// 这里是指向了第 0 层的数据,也就是真实的数据,其他层都是索引
current = current->forward[0];
if (current == NULL || current->key != key) {
int newLevel = randomLevel();
if (newLevel > skipList->level) {
for (int i = skipList->level + 1; i <= newLevel; i++) {
update[i] = skipList->header;
}
skipList->level = newLevel;
}
SkipListNode *newNode = createNode(key, value, newLevel);
for (int i = 0; i <= newLevel; i++) {
newNode->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = newNode;
}
}
}
查找操作从顶层开始,逐层向下查找,直到找到目标节点或者到达最底层。跳表的时间复杂度为 O(log n),其中 n 表示跳表中的节点数。
SkipListNode *search(SkipList *skipList, int key) {
SkipListNode *current = skipList->header;
for (int i = skipList->level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] != NULL && current->forward[i]->key < key) {
current = current->forward[i];
}
}
current = current->forward[0];
if (current != NULL && current->key == key) {
return current;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
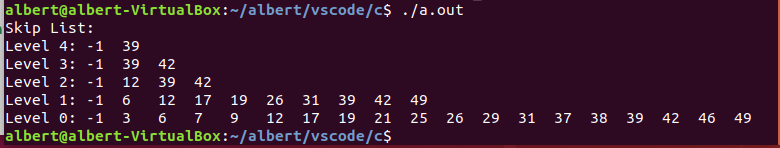
为了方便验证,这里增加跳表的打印程序,因为初始化跳表的时候都加了一个值为 -1 的 dummy 节点,所以这里也特别打印出来,以便于理解。
void printSkipList(SkipList *skipList) {
printf("Skip List:\n");
for (int i = skipList->level; i >= 0; i--) {
SkipListNode *current = skipList->header->forward[i];
printf("Level %d: %-4d", i, -1);
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%-4d", current->key);
current = current->forward[i];
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
SkipList *skipList = createSkipList();
insert(skipList, 3, 3);
insert(skipList, 6, 6);
insert(skipList, 7, 7);
insert(skipList, 9, 9);
insert(skipList, 12, 12);
insert(skipList, 19, 19);
insert(skipList, 17, 17);
insert(skipList, 26, 26);
insert(skipList, 21, 21);
insert(skipList, 25, 25);
insert(skipList, 29, 29);
insert(skipList, 37, 37);
insert(skipList, 31, 31);
insert(skipList, 42, 42);
insert(skipList, 39, 39);
insert(skipList, 49, 49);
insert(skipList, 46, 46);
insert(skipList, 38, 38);
printSkipList(skipList);
return 0;
}
然后构造测试用例,执行效果如下:
然后我们站在巨人的肩膀上了解一下 leveldb 中关于跳表的实现。
leveldb 跳表实现 #
Leveldb 本身是一个基于 LSM tree 的 KVDB,其中调表是它 memtable 在内存中的存放方式,它的源代码位于(https://github.com/google/leveldb/blob/main/db/skiplist.h)。
首先Node 结构和 SkipList 模板类如下, Node 本身用了 explicit 修饰,防止隐式转换。next_[1] 实际会根据节点高度动态分配更大空间。
Leveldb 本身实现了内存池 Arena,这里不做过多介绍。
struct Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) {}
Key const key; // 不可变的键值
std::atomic<Node*> next_[1]; // 柔性数组,存储各级指针
};
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList {
private:
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 }; // 最大高度限制
Node* const head_; // 头节点
std::atomic<int> max_height_; // 当前最大高度
Random rnd_; // 随机数生成器
};
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
: compare_(cmp),
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(1),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, nullptr);
}
}
节点查找 - FindGreaterOrEqual() #
找到第一个键值 ≥ 目标值的节点。
- 从最高层开始搜索
- 在当前层向右移动,直到下一个节点的键值 ≥ 目标值
- 记录每层的前驱节点到 prev 数组(用于插入)
- 下降到下一层继续搜索
- 到达第 0 层时返回找到的节点
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key,
Node** prev) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x;
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
节点插入 - Insert() #
-
查找插入位置:获取每层的前驱节点,并确认没有重复键
-
确定新节点高度:以 1/4 的概率增加高度(kBranching = 4)
-
更新最大高度: 如果新节点高度超过当前最大高度,更新 max_height_ 并设置高层前驱为头节点
-
链接新节点:
当设置 x->next_[i] 时,节点 x 还未对其他线程可见。
只有当我们通过 prev[i]->SetNext(i, x) 发布节点 x 时,才需要内存屏障,在这之前使用无屏障操作是安全的
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
高度随机化 - RandomHeight() #
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key, Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && rnd_.OneIn(kBranching)) {
height++;
}
return height;
}
- 高度为 1 的概率:
P(h=1) = 3/4 = 0.75 - 高度为 2 的概率:
P(h=2) = (1/4) × (3/4) = 3/16 = 0.1875 - 高度为 3 的概率:
P(h=3) = (1/4)² × (3/4) = 3/64 = 0.046875 - 高度为 4 的概率:
P(h=4) = (1/4)³ × (3/4) = 3/256 = 0.01171875 - …
- 高度为 kMaxHeight(12) 的概率:
P(h=12) = (1/4)^11 = 很小
LevelDB 选择 4 的原因:
减少指针内存占用,搜索性能降低不多(log₄n = ½ log₂n,只差常数因子)
| 分支因子 | 期望高度 | 平均指针数 | 搜索比较次数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | log₂n | n 个节点 ≈ 2n 指针 | 较少 |
| 4 | log₄n | n 个节点 ≈ 1.33n 指针 | 稍多 |
| 8 | log₈n | n 个节点 ≈ 1.14n 指针 | 更多 |
Last modified on 2026-01-24